The chemical formula of halon1301 is CBrF3 The IUPAC name for halon 1301 is bromotrifluoromethane Greenhouse Gas terms for the IASOA data vocabulary are take n from the Global Atmosphere Watch Station Information System (GAWSIS) For the full reference, please visit Greenhouse Gas Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 2530% Futtsu Thermal Power Station near Tokyo Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and oil produces more greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than any human activity, accounting for at least one quarter of all global emissionsThe greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know it
Components Of Air Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Water Vapor And Other Gases
What are the greenhouse gases names
What are the greenhouse gases names- The UK is phasing down HFCs by 79% by 30 from the average use between 09 to 12 The phase down also applies to mixtures containing these gases Industrial designation Chemical name (common Gummy Greenhouse Gas models of these gases Each molecule has a shorthand name, which also gives its recipe, or formula For example, ozone is also called O 3, where O stands for an oxygen atom and the little 3 means there are three of them Here are all the greenhouse gas molecules, their formulas, and a picture of its gumdrop model




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and tropospheric ozone (O 3) Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is a byproduct of the combustionor burningof fossil fuels such as coal and oil Since the Industrial Revolution, humans have burned increasingly greater amounts ofLearn more about climate change and discover ways to take action
Here are lists of HFCs and HFC blends, and their global warming potentials (GWP) For the purposes of the Ozone Protection and Synthetic Greenhouse Gas Management Act 19 and the Ozone Protection and Synthetic Greenhouse Gas Management Regulations 1995, 100year global warming potential is taken from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) fourthFluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that Reservoir gases make up about 13% of our total greenhouse gas emissions When land is flooded to make a reservoir, and plants and soil collect in the reservoir waters and downstream, this organic
Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most prominent Sources of atmospheric CO 2 include volcanoes, the combustion and decay of organic matter, respiration by aerobic (oxygenusing) organisms, and the burning of fossil fuels, clearing of land, and production of cement by humans Total fan capacity* (cubic feet/minute) = 8 x the greenhouse floor area (square feet) *fan capacity is measured at 010 0125 inches water static pressure Note use a large diameter fan with the smallest motor for the highest efficiency Example 30 foot x 100 foot hoophouse Total fan capacity needed = 8 x 30' x 100' = 24,000 cfmGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph




Chemistry Summer Assignment Ppt Download
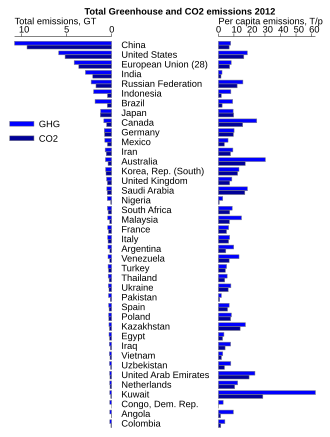



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
There are two types of emissions that impact on the environment Greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), which can trap additional heat from the sun in the earth's atmosphere, causing the 'greenhouse effect' and climate changeCO 2 is the main greenhouse gas produced by motor vehicles In 17, the average combined CO 2 emissions for a new light vehicle sold inGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without themThe reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphereWhen energy from theThese special trace gases are often referred to as greenhouse gases which are heattrapping gases that radiate the heat back to the Earth's surface, to another greenhouse gas molecule, or out to space The major greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO 2), water vapor (H 2 O), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) These greenhouse gas




Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica




48 Write The Formula Unit For The Following Chegg Com
You are About to View Greenhouse Gas Quantities from Suppliers Important Information about this Data Set Suppliers are facilities or entities that supply certains products (eg, fossil fuels or industrial gases) into the economy that, when combusted, released, orThis graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributorsArrhenius (1859–1927) in 16 Any gas in the Earth's atmosphere capable of trapping heat is defined as a greenhouse gas Major greenhouse gases include water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), and others A more detailed list of greenhouse gases may be




This Chart Gives Data On Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The United States From 1990 To 13 Which Brainly Com
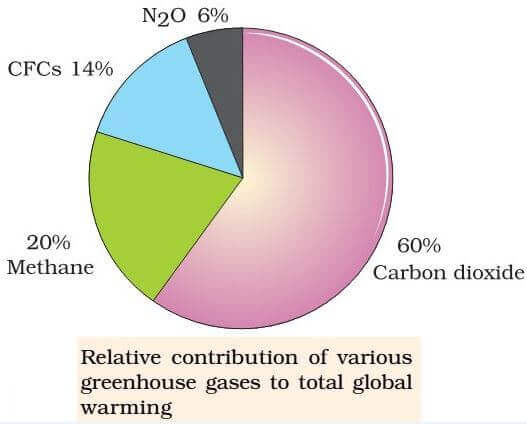



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias
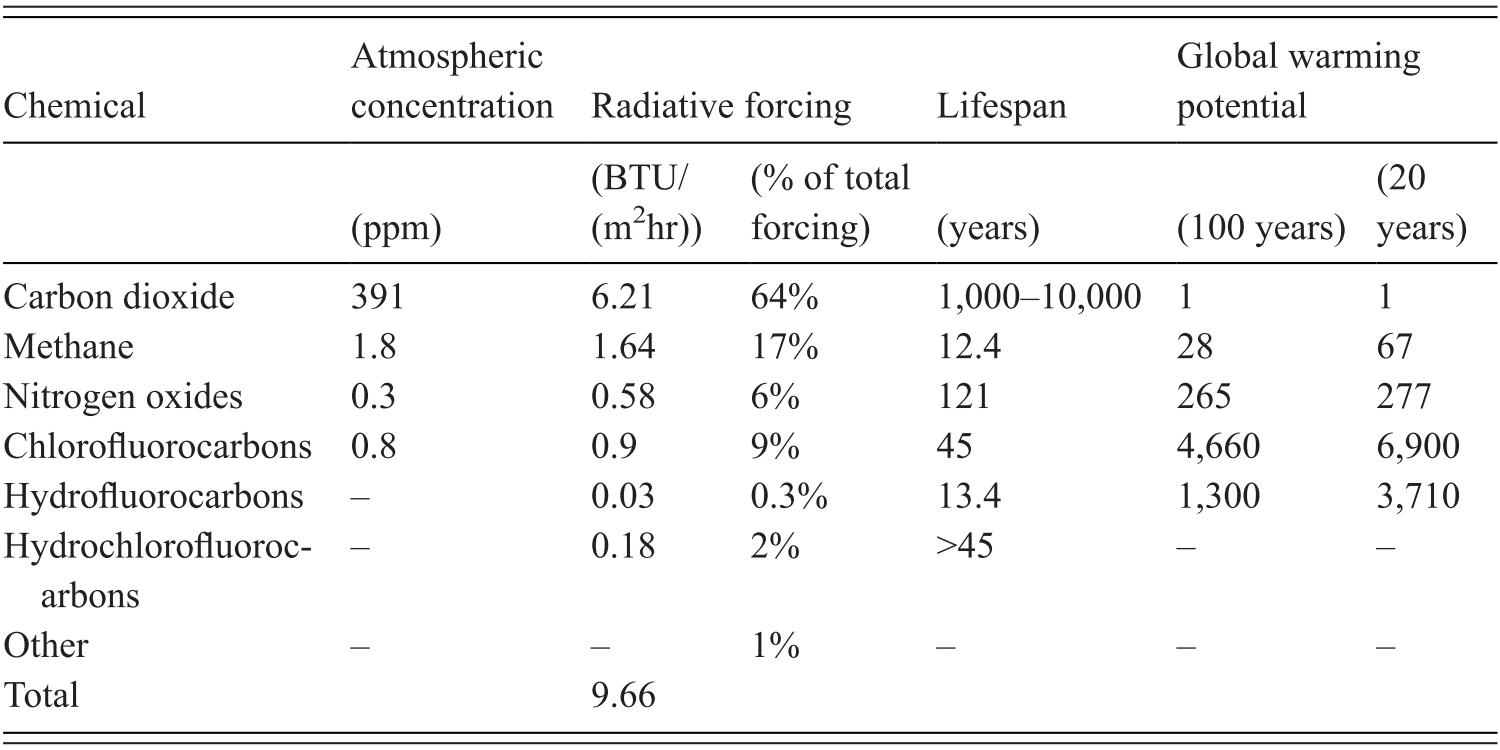
Table A1 List of Greenhouse Gases and their contribution to Scotland's net greenhouse gas emissions, 19 Name of Greenhouse Gas Chemical Formula Global Warming Potential (GWP) (Conversion factor to carbon dioxide equivalent) Contribution to Scotland's Net Greenhouse Gas Emissions, 19 (in MtCO 2 e) Percentage of Scotland's Net Greenhouse GasGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming oneFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6
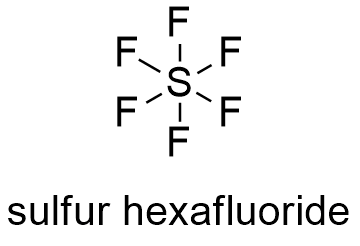



Sulfur Hexafluoride Formula



Planetary Science
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 14, CO 2 accounted for about 809% of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)Methane is a onecarbon compound in which the carbon is attached by single bonds to four hydrogen atomsIt is a colourless, odourless, nontoxic but flammable gas (bp 161℃) It has a role as a fossil fuel, a member of greenhouse gas and a bacterial metabolite(iv) training that supports greenhouse gas emissions reporting under these regulations or any other greenhouse gas reporting program (4) An accredited verification body who ceases to verify an emitter's GHG reports, after having verified their reports for 2 or more consecutive years, must not verify another GHG report for the emitter until




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
Carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), along with water vapour are known as greenhouse gases Due to human intervention, the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased remarkably causing the greenhouse effectMajor byproducts of burning fuels are greenhouse gases, including H 2 O(g), CO 2, CH 4, O 3, N 2 O and chlorofluorocarbons Compound Name Chemical Formula Water (vapor) H 2 O(g) Carbon Dioxide CO 2 Methane CH 4 Ozone O 3 Nitrous Oxide N 2 O Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFC 11 & CFC 12 CCl 3 F & CCl 2 F 2 Carbon dioxide (CO2) is also an important greenhouse gas It has a long lifetime in Earth's atmosphere Carbon dioxide strongly absorbs energy with a wavelength of 15 μm (micrometers) This makes carbon dioxide a good absorber of wavelengths falling in the infrared radiation region of the spectrum



Name Answer Key Ges 241 Introduction To Meteorology Quiz 1




Name Of Variables Symbols And Dimensional Equation Of Input Variables Download Table
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe uncertainty lies in the magnitude of the responseIt is well established that the global mean surface temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century by about 06 KGummy Greenhouse Gas models of these gases Each molecule has a shorthand name, which also gives its recipe, or formula For example, ozone is also called O3, where O stands for an oxygen atom and the little 3 means there are three of them Here are all the greenhouse gas molecules, their formulas, and a picture of its gumdrop model




Water Is Also A Greenhouse Gas Lios Soil




Boardworks As Chemistry Alkanes Chemistry Covalent Bonding Structural Formula
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They letWithout them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it When we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Join us on social! The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
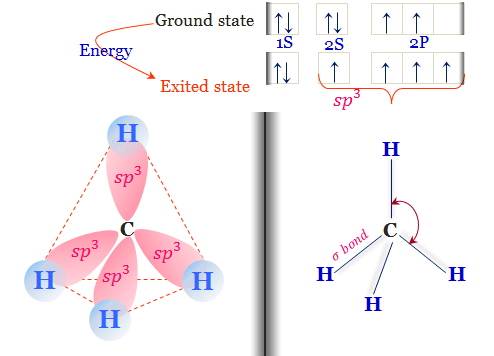



Methane Gas Source Formula Structure Properties Uses
Of CH 4 absorbs radiative energy 25 times more effectively than each molecule of CO 2, and CFC12 is 15,800 times more effective than CO 2 on a per molecule basis and, since molecules of the two gases have different mass, 5,750 times more effective on a per mass basis Figure 32 incorporates a simple extrapolation of current atmospheric transformation ratesGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3)Figure 71 Rise in the concentrations of greenhouse gases since the 18th century As we will see in section 73, simple theory shows that a rise in greenhouse gases should result in surface warming;




Carbon Dioxide Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases And Global Warming Potentials Gwp Sera Gazlari Ve Download Scientific Diagram
The answer may not be as clear as one might assume, because the top emitters change depending on how the data is collected and whatWhat are the chemical formulas for the three greenhouse gases shown in the image titled "Natural Greenhouse Effect"?Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a



Http Www Fao Org 3 I4260e I4260e Pdf



3
(Write their names too if you know them)Thes e gases occur naturally in earth's atmosphere 9 How does the amount of these three gases change in the image "Human Enhanced Greenhouse Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas emissions The key source of CO2 is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil andWho Receives the Small Business Climate Credit In addition to residential customers, eligible small businesses also receive a California Climate Credit A small business is defined by the CPUC as any nonresidential customer on a general service or agricultural rate, whose usage doesn't exceed kilowatts in more than three months out of the previous 12month period




The Chemical Formulas Of The Organic Acids Used Download Table
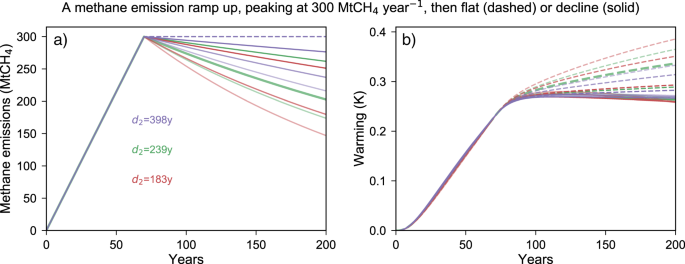



Improved Calculation Of Warming Equivalent Emissions For Short Lived Climate Pollutants Npj Climate And Atmospheric Science
Although greenhouse gases do not create a greenhouselike surface, they have a similar effect on keeping our planet warm, so the term greenhouse effect is a good description The greenhouse effect makes our planet's temperature brighter andSince the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases—including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is responsible for emitting the most greenhouse gases?R410A, sold under the trademarked names AZ, EcoFluor R410, Forane 410A, Genetron R410A, Puron, and Suva 410A, is a zeotropic but nearazeotropic mixture of difluoromethane (CH 2 F 2, called R32) and pentafluoroethane (CHF 2 CF 3, called R125) that is used as a refrigerant in air conditioning applications R410A cylinders are colored rose
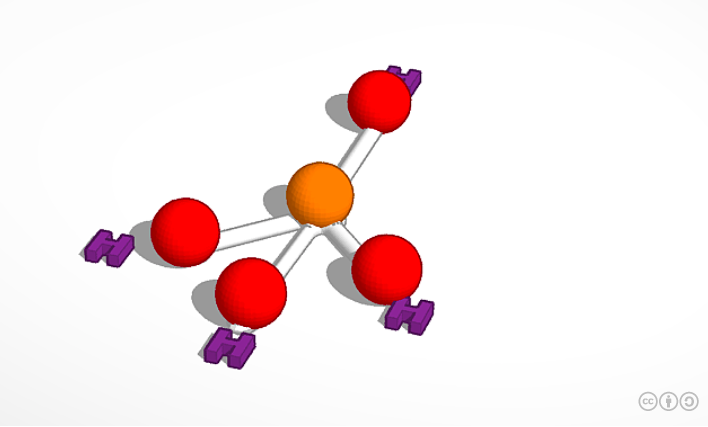



Future Engineers Name That Molecule Challenge Gallery Methane Ch4




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
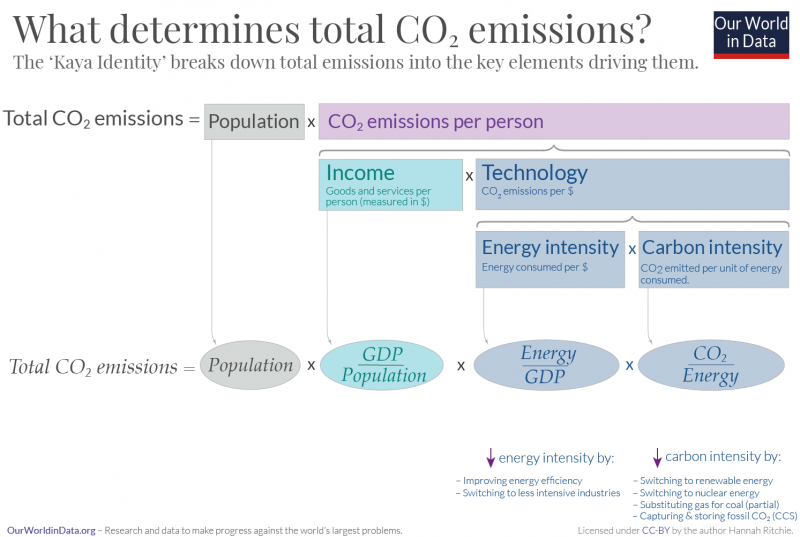



Emissions Drivers Our World In Data



Greenhouse Gases Atmosphere And Climates Chapter 8 Global Resources And The Environment




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



2



What Are The Differences Between Nitrous Oxide And Nitrogen Dioxide Greenhouse Gases Quora




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Calculation Tools Greenhouse Gas Protocol
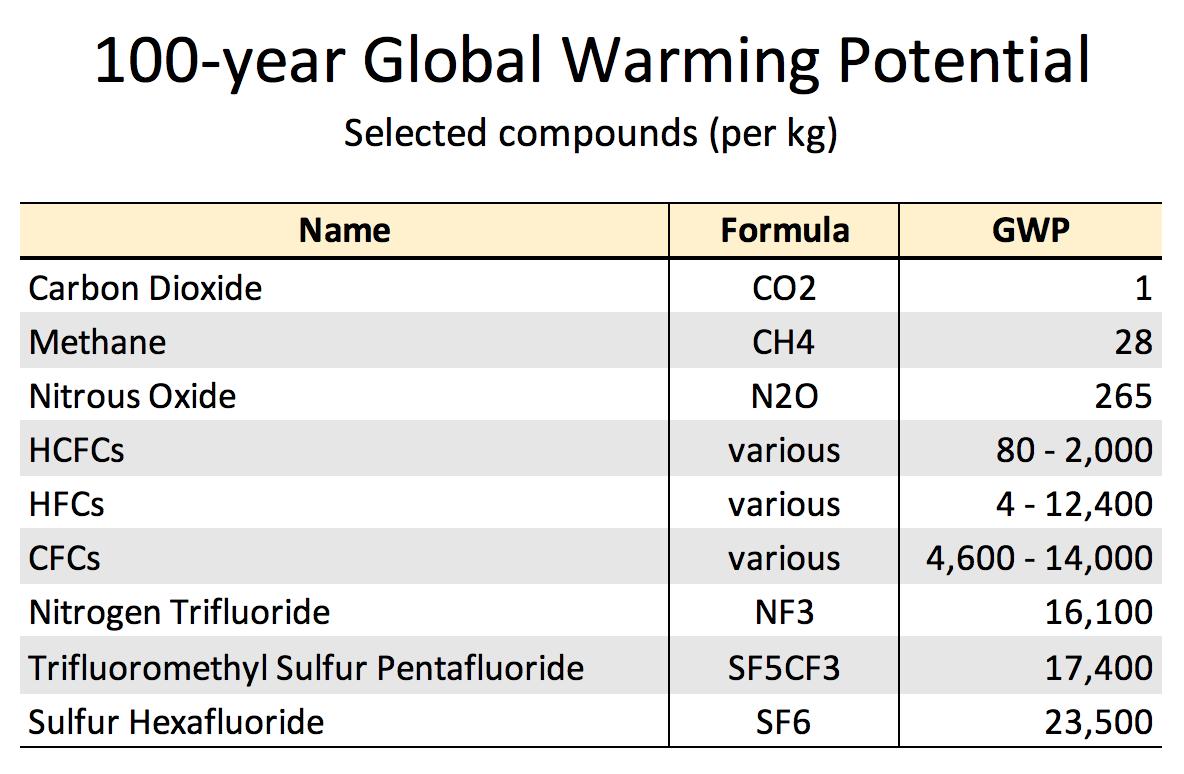



Dr Robert Rohde 5 By Why Do We Care About Sf Well Sf Is The Strongest Greenhouse Gas Ever Evaluated By The Ipcc Per Kilogram It Is 23 500 Times As



What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora
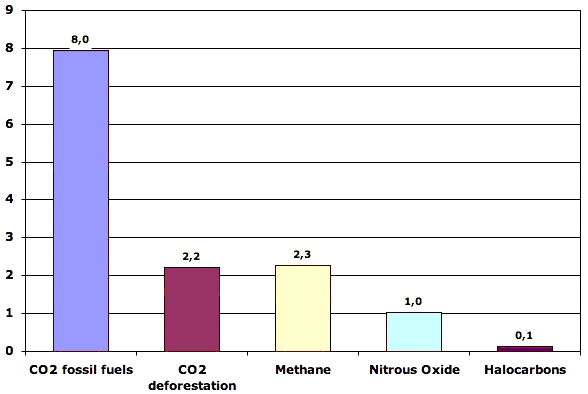



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



What S The Formula For Laughing Gas Quora




Gwp Values For Various Ghgs Download Table
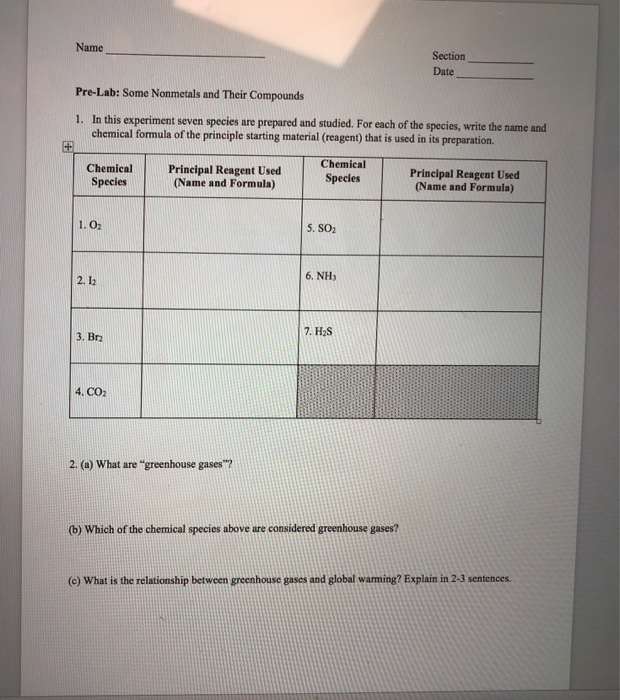



Name Section Date Pre Lab Some Nonmetals And Their Chegg Com




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Wpdefumef3y5 M



Ec Europa Eu Eurostat Documents Ks Ra 11 024 En Pdf



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Chemical Formulas And Symbols Used Download Table



Canviclimatic Gencat Cat Web Content 04 Actua Com Calcular Emissions Geh Guia De Calcul Demissions De Co2 Practical Guide Calculating Ghg Emissions Occc Pdf



Www Nea Gov Sg Docs Default Source Our Services Climate Change M R Appendix Ver 14 Feb 18 Pdf



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Main Greenhouse Gases Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




What S The Formula For Laughing Gas Quora




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef



4 41 Triple Only Understand How To Write The Structural And Displayed Formulae Of An Ester Given The Name Or Formula Of The Alcohol And Carboxylic Acid From Which It Is Formed And




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Topic Two Biogeochemical Cycles 2 3 Carbon Oxygen Cycle Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gas Interact




Nevada 19 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Report
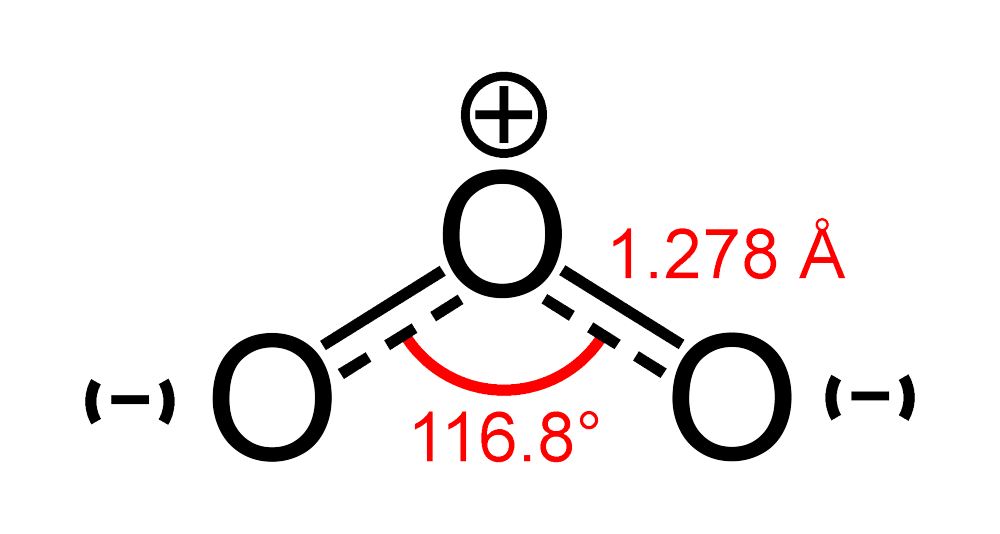



Ozone Wikipedia




Hydrogen Production And Applications Of Hydrogen Britannica
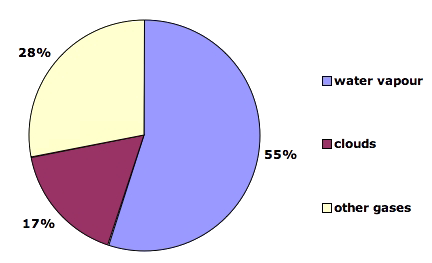



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
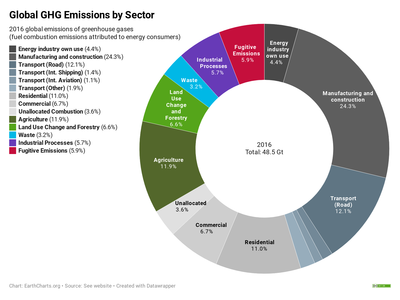



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Canviclimatic Gencat Cat Web Content 04 Actua Com Calcular Emissions Geh Guia De Calcul Demissions De Co2 Practical Guide Calculating Ghg Emissions Occc Pdf




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Ffectffect Ppt Download




Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids




Climate Change And Cdm Saadullah Ayaz
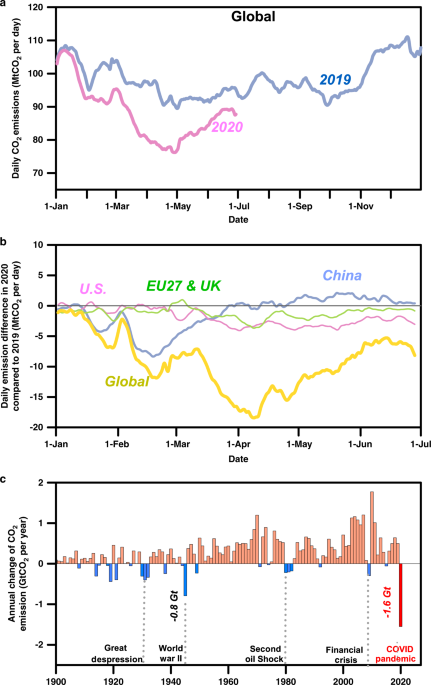



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Solved Give Example Of Least Two Atmospheric Gasses That Chegg Com




Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation



1
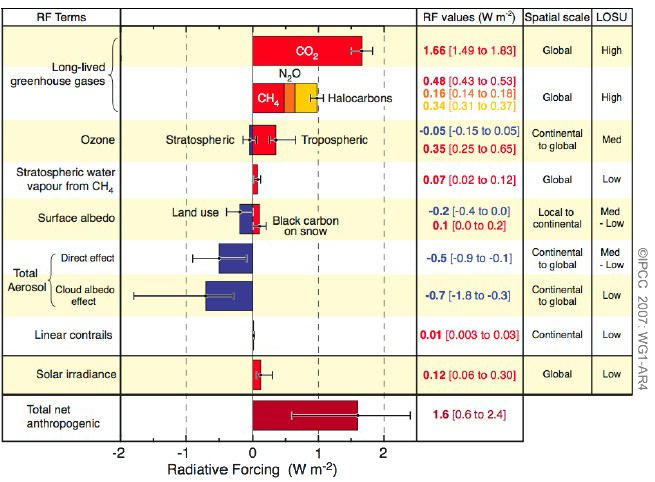



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



1



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




No2 Structure Nitrogen Dioxide Formula Structure Chemical Name Properties Uses




Global Warming The Level Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Has Gradually Increased As A Result Of Keywords Oceans Water Vapour Photosynthesis Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Evaluation Of The Global Protocol For Community Scale Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories Gpc Method For Chinese Cities Semantic Scholar




Methane Wikipedia



1



Components Of Air Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Water Vapor And Other Gases
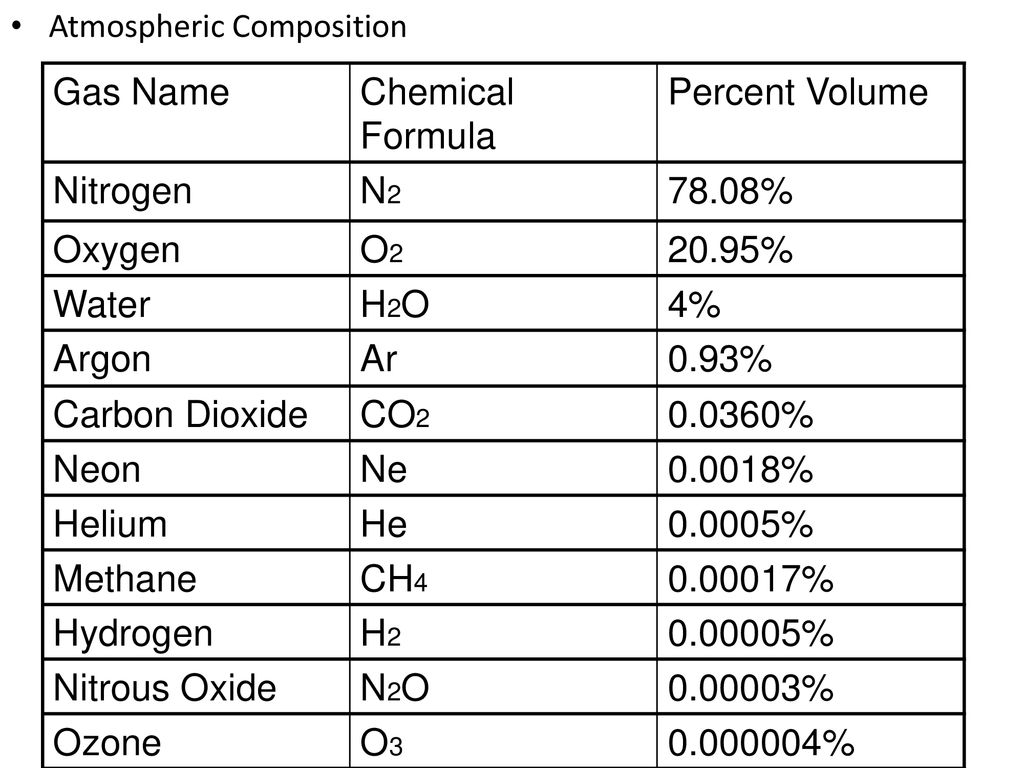



Gas Laws Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gases Atmosphere And Climates Chapter 8 Global Resources And The Environment
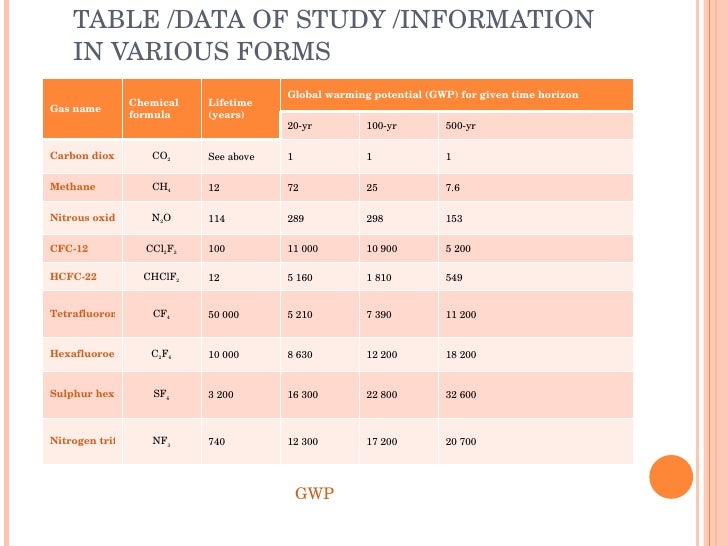



Green House Effect




Greenhouse Gas Methane Britannica




Cge Training Materials National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Quality




The Dynamic Earth External Radiant Energy From The




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Take Cornell Notes On This Video Nomk Nomk Ppt Download
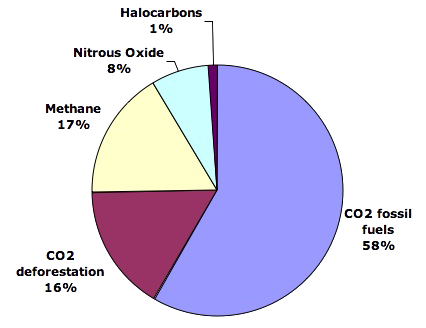



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
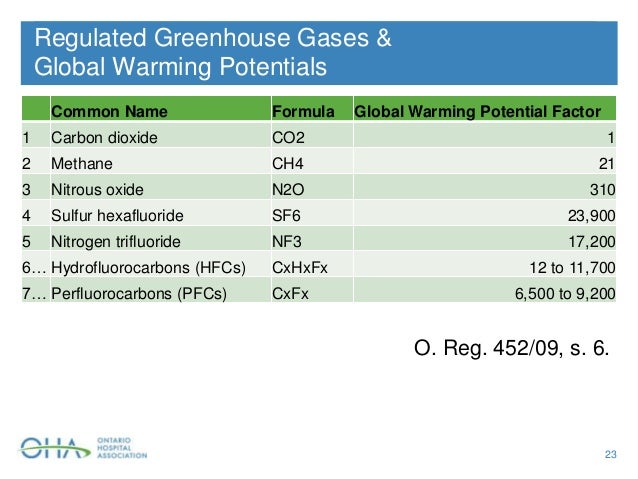



Carbon 101 Carbon Accounting For Hospitals




One Hundred Year Global Warming Potential Of Three Primary Greenhouse Download Table




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Greenhouse Gas Energy Saving Products




Greenhouse Effect Take Cornell Notes On This Video Nomk Nomk Ppt Download




Hydrochlorofluorocarbon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
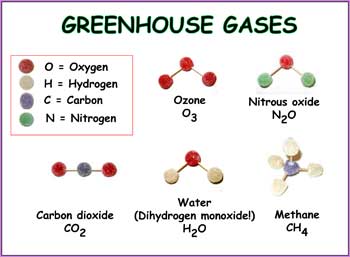



Get Your Gummy Greenhouse Gases Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Air Mixture
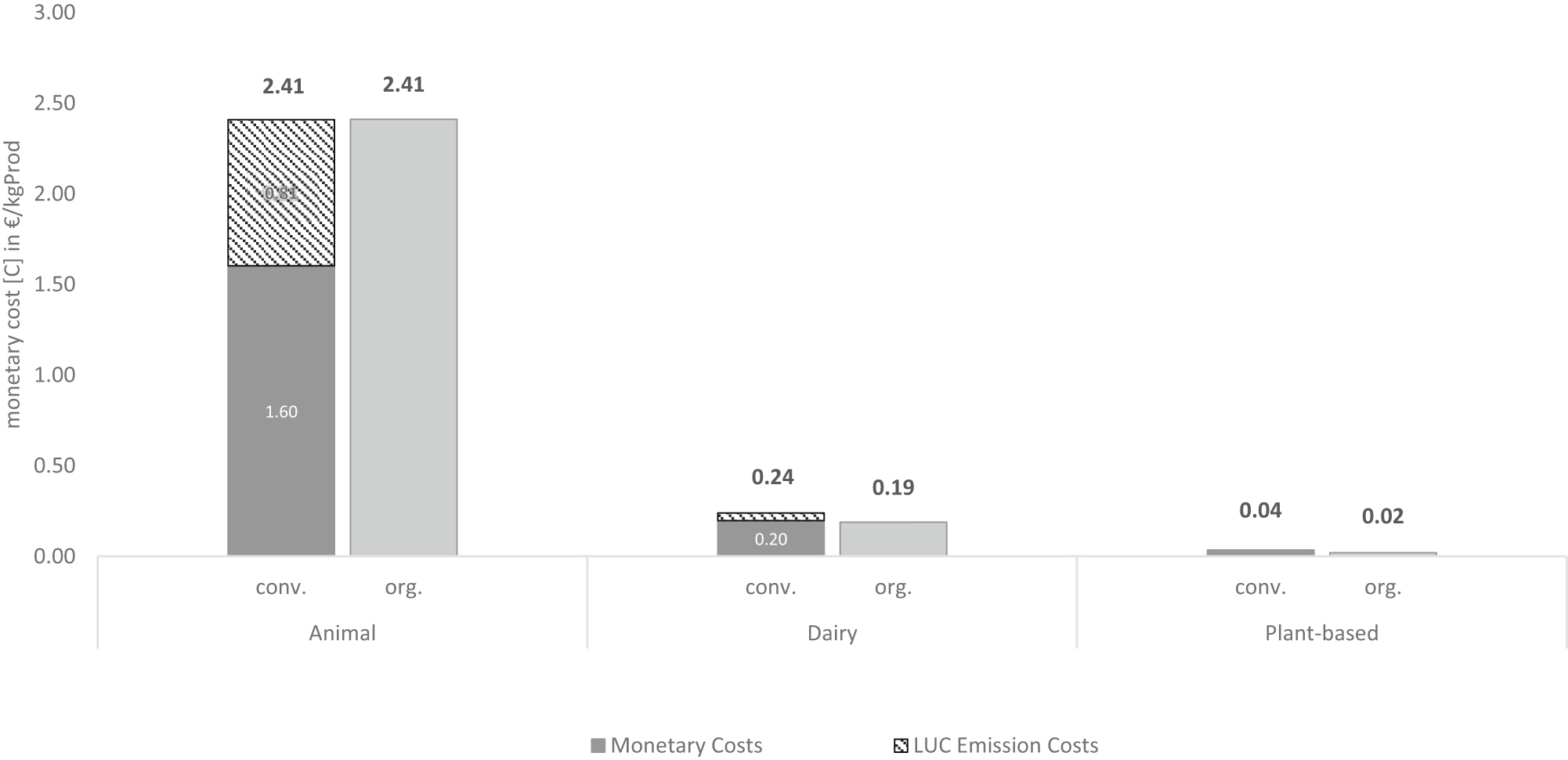



Calculation Of External Climate Costs For Food Highlights Inadequate Pricing Of Animal Products Nature Communications
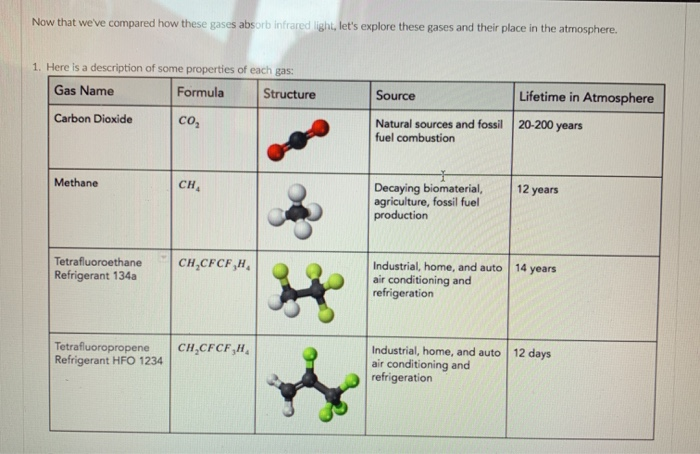



Based On This Information Which Gases Do You Think Chegg Com



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Future Engineers Name That Molecule Challenge Gallery Carbon Dioxide




Solved Hello If Anyone Can Give Proper Well Worked Out E Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿